
Wheel Selection
There is a vast choice of wheel size and material offerings. The key to choosing the right one is to understand your customer’s application and the environment they will be used in. This is a two-part course where you will learn the basic caster wheel terminology, characteristics, and types.
Please make sure to download the Wheel Measurements PDF in section 1 or here. You will need the diagram for your final quiz.
Wheel Measurements
Wheel Measurment PDF for final quiz
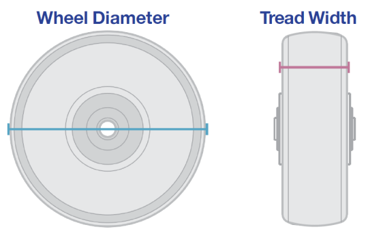
Wheel Size
– Outside Diameter x Tread Width
Hub length
– Distance from one end of hub to the other
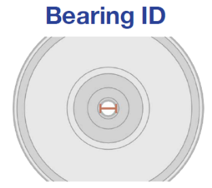
Bearing ID
– Inner Diameter of wheel bearing
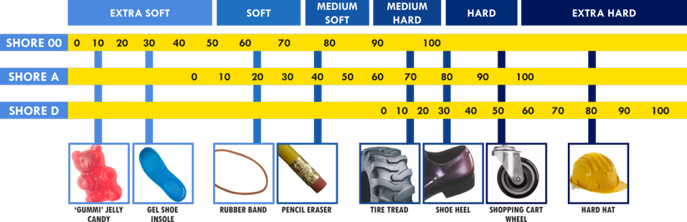
Durometer
– A measurement of the hardness of a material.
Wheel Face
– This refers to the shape of the tread on a wheel.
– Crowned treads require less force to turn, but flat treads can hold higher loads.


Load Capacity
– Is the rated capacity per wheel while it is rolling
– How to calculate load capacity requirements
- = Max weight of the equipment/(number of wheels – 1)
Rollability (Breakaway/Sustained Rolling Force)
– How easy is it to move?
– Refers to the amount of force required to start (breakaway) or keep (sustained) the unit rolling
– Certain materials help reduce these force requirements
Floor Protection
Shock Absorption
Corrosion Resistance
– Does the wheel hold up well in wash down applications?
Chemical/Water Resistance
– Different materials can resist harsh chemicals better than others.
Temperature Range
– The range of temperature where the wheel can perform without failure varies by material.
Harder Wheels
– Higher load capacity
– Lower breakaway/sustained rolling force
– Reduced floor protection
– Less shock absorption

